Published 27 November 2023
The Road to Relief: Managing Facial Folliculitis Made Easy
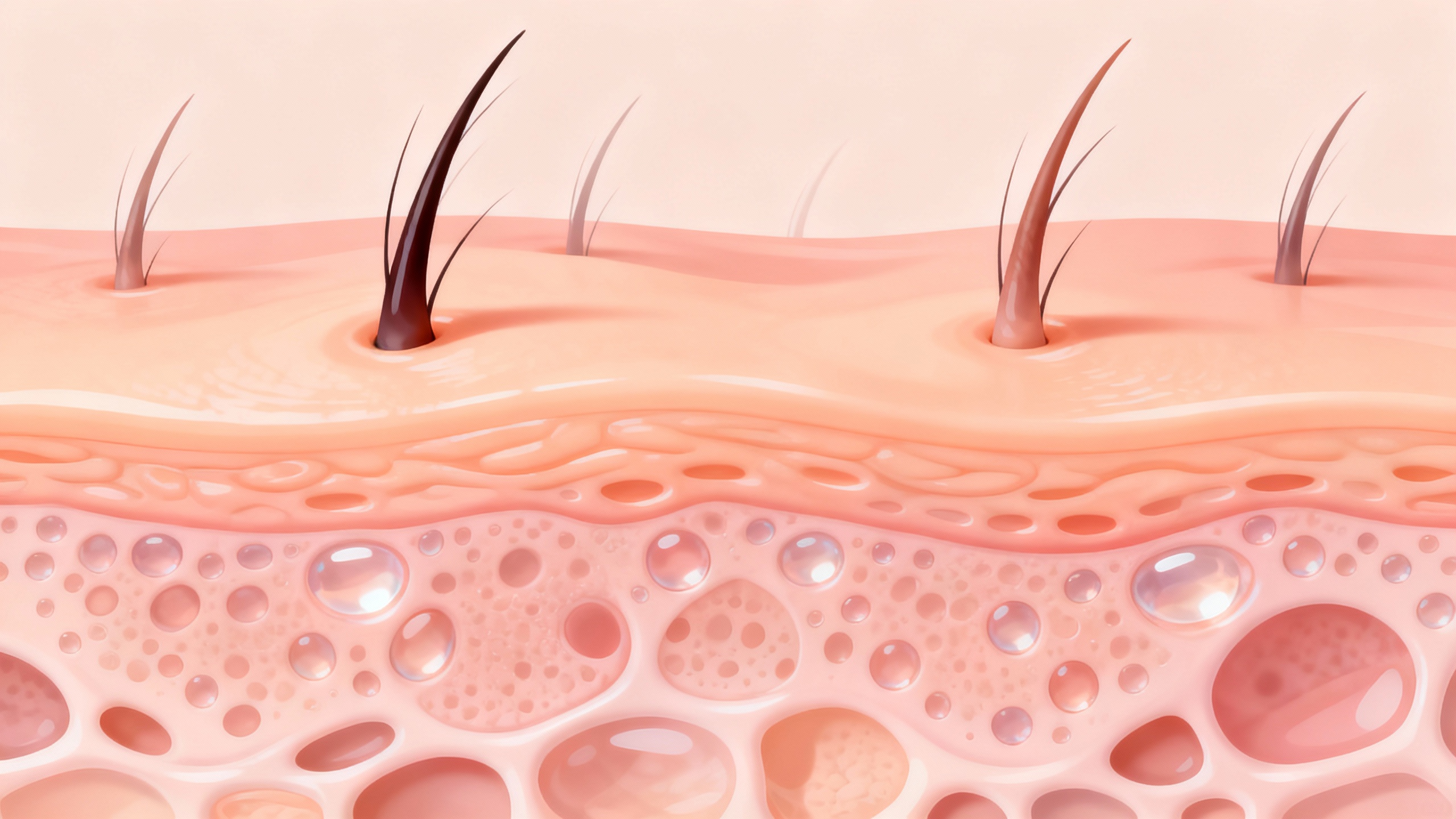
Understanding Facial Folliculitis
Facial folliculitis is a common condition characterized by the inflammation and infection of hair follicles on the face. It can cause discomfort, redness, and the formation of small pustules. Understanding the causes, risk factors, and identifying the symptoms of facial folliculitis is essential for effective management.
What is Facial Folliculitis?
Facial folliculitis refers to the inflammation and infection of hair follicles on the face. It occurs when bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus, enter the hair follicles, leading to redness, swelling, and the formation of pustules. These pustules may be filled with pus and can cause itching and tenderness.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of facial folliculitis. Common causes and risk factors include:
-
Bacterial infection: The most common cause of facial folliculitis is a bacterial infection, particularly by Staphylococcus aureus. This bacterium is naturally present on the skin but can multiply and cause infection when the hair follicles become inflamed or damaged.
-
Ingrown hairs: Ingrown hairs occur when the hair grows back into the skin, leading to inflammation and blockage of the hair follicles. This increases the risk of bacterial infection and the development of folliculitis.
-
Excessive oil production: Excessive oil production can clog the hair follicles and create an environment conducive to bacterial growth. This can be a contributing factor to the development of facial folliculitis.
-
Skin damage and irritation: Any damage or irritation to the skin, such as from shaving, can disrupt the natural barrier and make the hair follicles more susceptible to infection.
-
Weakened immune system: Individuals with a weakened immune system, such as those with diabetes or HIV/AIDS, are at a higher risk of developing folliculitis due to reduced ability to fight off infection.
Identifying Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of facial folliculitis is important for early intervention and appropriate management. Common symptoms include:
-
Redness and swelling: The affected area may appear red and swollen, indicating inflammation of the hair follicles.
-
Pustules: Small pustules may develop on the skin, resembling small red bumps or whiteheads. These pustules may contain pus and can be itchy or tender.
-
Itching and discomfort: Facial folliculitis can cause itching and discomfort, leading to a desire to scratch the affected area. However, scratching can worsen the condition and increase the risk of spreading the infection.
-
Pain and tenderness: In some cases, facial folliculitis may cause pain and tenderness around the affected hair follicles.
If you suspect you have facial folliculitis, it is important to consult a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Early intervention can help prevent the condition from worsening and reduce the risk of complications.
By understanding the nature of facial folliculitis, its causes, risk factors, and identifying the symptoms, individuals can take appropriate measures to manage the condition. It is crucial to follow a proper skincare routine, seek antibacterial treatments, and soothe skin irritation to promote healing and prevent future flare-ups. For more information on managing facial folliculitis, check out our article on coping with folliculitis.
Managing Facial Folliculitis
To effectively manage facial folliculitis, implementing a proper skincare routine is essential. This routine should include cleansing, exfoliating, and moisturizing the affected areas regularly. By following these steps, you can help reduce inflammation, prevent bacterial growth, and promote healing.
Cleansing
When dealing with facial folliculitis, it’s crucial to keep the affected area clean. Use a mild, non-comedogenic facial cleanser to gently cleanse the skin. Avoid harsh cleansers or scrubbing vigorously, as this can further irritate the follicles. Make sure to wash your face twice a day, in the morning and before bed, to remove dirt, oil, and bacteria that can contribute to the condition.
Exfoliating
Regular exfoliation is an important step in managing facial folliculitis. Exfoliating helps remove dead skin cells, unclog pores, and prevent the buildup of bacteria. However, it’s important to choose gentle exfoliating products to avoid further irritation. Look for exfoliants that contain salicylic acid or glycolic acid, as these ingredients can help promote cell turnover and prevent follicle blockage.
Moisturizing
Moisturizing is crucial for maintaining the skin’s hydration and promoting its overall health. Look for oil-free, non-comedogenic moisturizers specifically formulated for acne-prone or sensitive skin. These moisturizers help to balance the skin’s moisture levels without clogging the follicles. Applying a moisturizer after cleansing and exfoliating can help soothe the skin and reduce dryness or irritation.
By incorporating a proper skincare routine that includes cleansing, exfoliating, and moisturizing, you can effectively manage facial folliculitis. However, if the condition persists or worsens, it’s important to seek medical advice from a dermatologist. They can provide additional guidance and recommend appropriate treatments to address the underlying causes of facial folliculitis.
For additional information on coping with folliculitis, relief strategies, and self-care tips, check our related articles on coping with folliculitis and relief for folliculitis.
Antibacterial Treatments
To effectively manage facial folliculitis, antibacterial treatments play a crucial role in reducing inflammation and preventing infection. There are two main types of antibacterial treatments commonly used for facial folliculitis: topical antibiotics and oral antibiotics.
Topical Antibiotics
Topical antibiotics are applied directly to the affected areas of the skin to target and eliminate the bacteria causing the folliculitis. These antibiotics come in the form of creams, gels, or ointments, and they work by killing the bacteria or inhibiting their growth.
Common topical antibiotics used for facial folliculitis include erythromycin and clindamycin. These medications are typically applied twice a day, following proper cleansing and drying of the affected areas. It’s important to consult a dermatologist before using any topical antibiotics to determine the most suitable treatment for your specific condition.
Oral Antibiotics
In cases where the facial folliculitis is more severe or widespread, oral antibiotics may be prescribed. Oral antibiotics are ingested and work systemically to combat the bacterial infection from within the body.
The choice of oral antibiotics depends on the severity and type of folliculitis. Antibiotics such as doxycycline, minocycline, or cephalexin are commonly prescribed for facial folliculitis. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and duration as instructed by the healthcare professional. Completion of the full course of antibiotics is essential to ensure effective treatment and prevent the development of antibiotic resistance.
It’s worth noting that prolonged use of antibiotics can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria on the skin and may lead to other complications. Therefore, it is important to use antibiotics judiciously and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
When considering antibacterial treatments for facial folliculitis, it’s essential to consult a dermatologist to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific condition. Antibiotics should always be used in conjunction with other management strategies, such as proper skincare, to maximize the effectiveness of treatment.
Remember, managing facial folliculitis requires a comprehensive approach that includes proper skincare, soothing skin irritation, and making necessary lifestyle adjustments to prevent further flare-ups and promote healing.
Soothing Skin Irritation
When dealing with facial folliculitis, it’s important to address the accompanying skin irritation to promote healing and provide relief. Here are some soothing remedies that can help alleviate discomfort caused by facial folliculitis:
Warm Compress
Applying a warm compress to the affected areas can help soothe skin irritation caused by facial folliculitis. The warmth helps to increase blood circulation, reduce inflammation, and promote healing. To use a warm compress, soak a clean washcloth in warm water, wring out the excess, and gently place it on the affected areas of your face. Leave it on for 10 to 15 minutes, repeating the process a few times a day for relief.
Aloe Vera
Known for its soothing and healing properties, aloe vera is a natural remedy that can provide relief for skin irritation caused by facial folliculitis. Apply a thin layer of pure aloe vera gel to the affected areas of your face and let it dry. The gel will help calm inflammation, reduce redness, and promote healing. You can repeat this process multiple times a day for optimal results.
Calamine Lotion
Calamine lotion is another effective option for soothing skin irritation associated with facial folliculitis. This over-the-counter lotion contains a combination of zinc oxide and ferric oxide, which work together to relieve itching and reduce inflammation. Apply a thin layer of calamine lotion to the affected areas of your face and allow it to dry. You can use calamine lotion as needed throughout the day to alleviate discomfort and promote healing.
By incorporating these soothing remedies into your skincare routine, you can help manage the skin irritation associated with facial folliculitis. It’s important to note that while these remedies can provide temporary relief, they may not address the underlying cause of folliculitis. If your symptoms persist or worsen, it’s advisable to consult a dermatologist for further evaluation and medical treatment options. For more information on managing facial folliculitis and coping strategies, refer to our article on coping with folliculitis.
Lifestyle Adjustments
When managing facial folliculitis, certain lifestyle adjustments can help alleviate symptoms and prevent further irritation. By making small changes to your daily routine, you can promote healing and reduce the likelihood of future flare-ups. Consider the following tips:
Avoiding Irritants
To minimize the risk of aggravating facial folliculitis, it’s important to avoid irritants that can exacerbate the condition. This includes harsh chemicals found in skincare products, such as fragrances and alcohol-based cleansers. Opt for gentle, non-comedogenic products specifically formulated for sensitive or acne-prone skin. Look for products labeled as “oil-free” or “non-comedogenic” to prevent clogging of the hair follicles. Additionally, avoid touching or picking at the affected areas, as this can introduce bacteria and worsen the inflammation.
Gentle Shaving Techniques
Improper shaving techniques can contribute to the development of facial folliculitis. To minimize irritation, adopt gentle shaving practices. Use a clean, sharp razor and ensure it is not dull or rusty. Before shaving, soften the hair and open the pores by applying a warm towel to your face or taking a warm shower. Use a shaving cream or gel to provide lubrication and protect the skin. Shave in the direction of hair growth to reduce the risk of hair follicle damage. After shaving, rinse your face with cool water and apply a soothing moisturizer. For more tips on managing folliculitis on the face, visit our article on coping with folliculitis.
Cleanliness and Hygiene
Maintaining proper cleanliness and hygiene is essential in managing facial folliculitis. Wash your face twice a day with a mild, non-soap cleanser to remove dirt, oil, and bacteria. Avoid scrubbing too vigorously, as this can irritate the skin and worsen the condition. Pat your face dry with a clean towel instead of rubbing, which can cause friction and potential inflammation. It’s also important to regularly clean and disinfect any tools that come into contact with your face, such as makeup brushes or razors. This helps prevent the spread of bacteria and reduces the risk of infection.
By implementing these lifestyle adjustments, you can support the healing process and manage facial folliculitis more effectively. However, if symptoms persist or worsen despite these measures, it is advisable to seek medical advice. In the next section, we will explore when to consult a dermatologist and the available medical treatment options.
Seeking Medical Advice
While self-care measures can help manage mild cases of facial folliculitis, it’s important to know when it’s necessary to seek professional medical advice. Consulting a dermatologist can provide you with expert guidance and ensure appropriate treatment for your condition. In this section, we will explore when to consult a dermatologist, the medical treatment options available, and the importance of follow-up care and maintenance.
When to Consult a Dermatologist
If you’re experiencing persistent or severe symptoms of facial folliculitis that do not improve with self-care measures, it is recommended to schedule an appointment with a dermatologist. Additionally, if you notice any signs of infection, such as increasing redness, swelling, or pus-filled lesions, seeking medical advice is crucial.
A dermatologist can accurately diagnose facial folliculitis and determine the underlying cause of your condition. They will also be able to provide you with personalized treatment options based on the severity and specific characteristics of your folliculitis.
Medical Treatment Options
Dermatologists may prescribe various medical treatment options to manage facial folliculitis effectively. These can include:
-
Topical Antibiotics: Antibacterial creams or ointments containing ingredients like benzoyl peroxide, clindamycin, or erythromycin can be prescribed to reduce the bacteria responsible for folliculitis.
-
Oral Antibiotics: In more severe cases or when the infection has spread, oral antibiotics may be prescribed. These medications work to eliminate the bacteria causing the folliculitis from within the body.
It’s important to follow the prescribed treatment plan and complete the full course of antibiotics to ensure effective eradication of the infection.
Follow-up Care and Maintenance
After receiving medical treatment for facial folliculitis, it’s essential to follow up with your dermatologist to ensure proper healing and to address any concerns or questions you may have. They can assess your progress and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
In addition to medical treatment, your dermatologist may provide guidance on long-term maintenance strategies to prevent future flare-ups. This may include recommendations for proper skincare routines, avoiding known triggers, and lifestyle adjustments.
By maintaining regular follow-up appointments and adhering to the advice and treatment provided by your dermatologist, you can effectively manage facial folliculitis and minimize the risk of recurrence.
Remember, each case of facial folliculitis is unique, and the treatment plan may vary depending on individual factors. It’s important to consult a dermatologist for personalized care and guidance specific to your condition.
